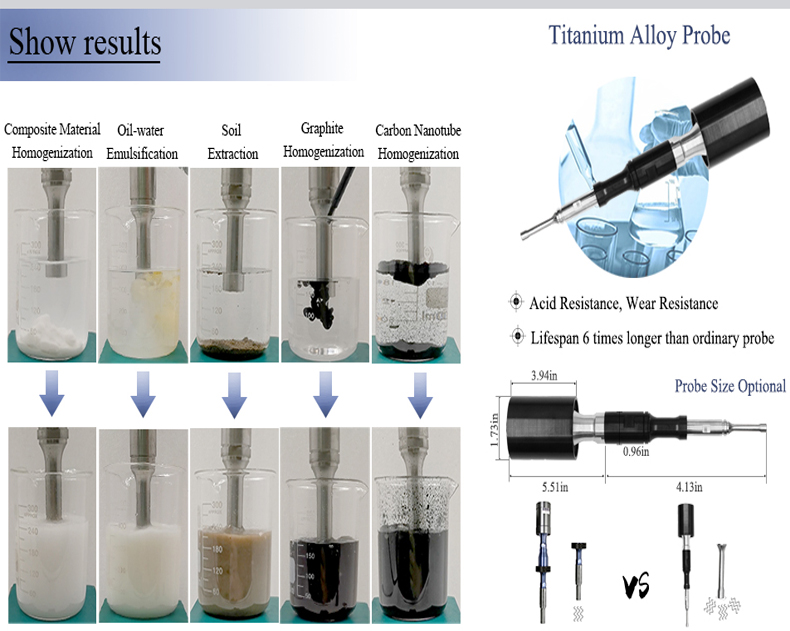
probe sonicator for cell lysis
2025-12-25
The use of probe sonicator is one of the commonly used physical methods for achieving efficient cell lysis, particularly suitable for the fragmentation of samples such as bacteria, mammalian cells, plant tissues, and viruses.
probe sonicator for cell lysis refers to the process of breaking down the cell membrane or wall to release internal components such as proteins, DNA, and RNA. Efficient cell lysis is a prerequisite for extracting target biomolecules in molecular biology, biochemistry, and pharmaceutical research.
The probe sonicator ultrasonic cell disruptor generates cavitation effect through high-frequency vibration, forming tiny bubbles in the liquid and violently rupturing, thereby generating strong shear force and directly damaging the cell structure. Compared to other methods such as chemical cracking and enzymatic hydrolysis, it has the advantages of fast speed, high efficiency, and no need to add external reagents.
Functional mechanism and operational points
Working principle of probe sonicator for cell lysis: The piezoelectric transducer is used to convert electrical energy into mechanical vibration, which is transmitted to the sample through a titanium alloy probe, triggering local high temperature, high pressure, and shock waves, resulting in cell breakage












